Experimental evolution
Experimental evolution is a powerful research approach for many questions about the evolution of social behavior, multicellularity and predator-prey interactions among microbes.
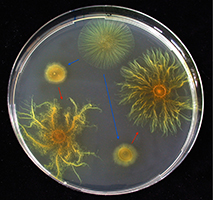
Experimental evolution with microbes features known and revivable ancestors, defined selective environments, frozen storage of viable evolving populations and communities for later analysis, large population sizes and mutation supply, easy replication and tractable molecular analysis of evolutionary change. Evolution experiments with myxobacteria – external pageMyxoEEscall_made – have been used to address many evolutionary questions and are summarised at external pagemyxoee.orgcall_made.
We examine how variable levels and forms of investment in cooperative behaviors evolve in response to different evolutionary forces.
external pageHidden paths to endless forms most wonderful: ecology latently shapes evolution of multicellular development in predatory bacteriacall_made
M La Fortezza, O Rendueles, H Keller, GJ Velicer. 2022. Communications Biology
external pageAllopatric divergence of cooperators confers cheating resistance and limits effects of a defector mutationcall_made
KA Schaal, YTN Yu, M Vasse, GJ Velicer. 2022. BMC Ecology and Evolution
external pageSocial selection within aggregative multicellular development drives morphological evolutioncall_made
M La Fortezza, GJ Velicer. 2021. Proc Roy Soc B
external pageIndirect evolution of social fitness inequalities and facultative social exploitationcall_made
Nair RR, F Fiegna, GJ Velicer. 2018. Proc Roy Soc B
external pageSocial complementation and growth advantages promote socially defective bacterial isolatescall_made
Kraemer SA and GJ Velicer. 2014. Proc Roy Soc B
external pageExperimental evolution of selfish policing in social bacteriacall_made
Manhes P and GJ Velicer. 2011. PNAS
external pageEvolution of an obligate social cheater to a superior cooperatorcall_made
Fiegna F, YTN Yu, SV Kadam and GJ Velicer. 2006. Nature
external pageCompetitive fates of bacterial social parasites: persistence and self-induced extinction of Myxococcus cheaterscall_made
Fiegna F and GJ Velicer. 2003. Proc Roy Soc B
external pageDevelopmental cheating in the social bacterium Myxococcus xanthuscall_made
Velicer GJ, L Kroos and RE Lenski. 2000. Nature
external pageLoss of social behaviors by Myxococcus xanthus during evolution in an unstructured habitatcall_made
Velicer GJ, L Kroos and RE Lenski. 1998. PNAS
We investigate factors shaping the evolution of developmental phenotypes and interactions.
external pageRibonuclease D Processes a Small RNA Regulator of Multicellular Development in Myxobacteriacall_made
SM Cossey, GJ Velicer, YTN Yu. 2023. Genes
external pageHidden paths to endless forms most wonderful: ecology latently shapes evolution of multicellular development in predatory bacteriacall_made
M La Fortezza, O Rendueles, H Keller, GJ Velicer. 2022. Communications Biology
external pageSocial selection within aggregative multicellular development drives morphological evolutioncall_made
M La Fortezza, GJ Velicer. 2021. Proc Roy Soc B
external pageIndirect evolution of social fitness inequalities and facultative social exploitationcall_made
Nair RR, F Fiegna, GJ Velicer. 2018. Proc Roy Soc B
external pageEvolution of an obligate social cheater to a superior cooperatorcall_made
Fiegna F, YTN Yu, SV Kadam and GJ Velicer. 2006. Nature
external pageDevelopmental cheating in the social bacterium Myxococcus xanthuscall_made
Velicer GJ, L Kroos and RE Lenski. 2000. Nature
external pageLoss of social behaviors by Myxococcus xanthus during evolution in an unstructured habitatcall_made
Velicer GJ, L Kroos and RE Lenski. 1998. PNAS
Negative and positive frequency dependence of social fitness readily evolves among closely related conspecifics.
external pagePredatory bacteria select for sustained prey diversitycall_made
RR Nair, GJ Velicer. 2021. Microorganisms
external pageExperimental evolution of selfish policing in social bacteriacall_made
Manhes P and GJ Velicer. 2011. PNAS
external pageSociobiology of the myxobacteriacall_made
Velicer GJ and M Vos. 2009. Annual Review of Microbiology
external pageEvolution of an obligate social cheater to a superior cooperatorcall_made
Fiegna F, YTN Yu, SV Kadam and GJ Velicer. 2006. Nature
external pageCompetitive fates of bacterial social parasites: persistence and self-induced extinction of Myxococcus cheaterscall_made
Fiegna F and GJ Velicer. 2003. Proc Roy Soc B
external pageDevelopmental cheating in the social bacterium Myxococcus xanthuscall_made
Velicer GJ, L Kroos and RE Lenski. 2000. Nature
We are interested in how the genotype-phenotype networks of myxobacterial social/developmental traits are structured and evolve in response to various evolutionary forces.
external pageAntagonistic, synergistic, and social pleiotropy in microbial cheaterscall_made
P Manhes, KA Schaal, GJ Velicer. 2022. bioRxiv
external pageIndirect evolution of social fitness inequalities and facultative social exploitationcall_made
Nair RR, F Fiegna, GJ Velicer. 2018. Proc Roy Soc B
external pageParallel emergence of negative epistasis across experimental lineagescall_made
Zee PC and GJ Velicer. 2017. Evolution
external pagePervasive, yet idiosyncrative, epistatic pleiotropy during adaptation in a behaviourally complex microbecall_made
Zee PC, J Liu and GJ Velicer. 2017. Journal of Evolutionary Biology
external pageEvolution by flight and fight: diverse mechanisms of adaptation by actively motile microbescall_made
Rendueles O and GJ Velicer. 2017. The ISME Journal
external pageRapid and widespread de novo evolution of kin discriminationcall_made
Rendueles O, PC Zee, I Dinkelacker, M Amherd, S Wielgoss and GJ Velicer. 2015. PNAS
external pageA shift from magnitude to sign epistasis during adaptive evolution of a bacterial social traitcall_made
Zee PC, H Mendes-Soares, YTN Yu, H Keller, SA Kraemer, S Ossowski, K Schneeberger and GJ Velicer. 2014. Evolution
external pageDevelopmental cheating in the social bacterium Myxococcus xanthuscall_made
Velicer GJ, L Kroos and RE Lenski. 2000. Nature
external pageLoss of social behaviors by Myxococcus xanthus during evolution in an unstructured habitatcall_made
Velicer GJ, L Kroos and RE Lenski. 1998. PNAS
Motility is fundamental to the social lives of myxobacteria. We ask how the motility behaviors and systems of Myxococcus evolve in response to different forms of selection.
external pageHidden paths to endless forms most wonderful: Complexity of bacterial motility shapes diversification of latent phenotypescall_made
O Rendueles, GJ Velicer. 2020. BMC Evolutionary Biology
external pageEvolution by flight and fight: diverse mechanisms of adaptation by actively motile microbescall_made
Rendueles O and GJ Velicer. 2017. The ISME Journal
external pageExperimental evolution of a microbial predator’s ability to find preycall_made
Hillesland KL, GJ Velicer and RE Lenski. 2009. Proc Roy Soc B
external pageEvolution of novel cooperative swarming in the bacterium Myxococcus xanthuscall_made
Velicer GJ and YTN Yu. 2003. Nature
external pageLoss of social behaviors by Myxococcus xanthus during evolution in an unstructured habitatcall_made
Velicer GJ, L Kroos and RE Lenski. 1998. PNAS
Kin discrimination readily evolves in experimental populations of microbes in a variety of forms.
external pageIndirect evolution of social fitness inequalities and facultative social exploitationcall_made
Nair RR, F Fiegna, GJ Velicer. 2018. Proc Roy Soc B
external pageEvolution by flight and fight: diverse mechanisms of adaptation by actively motile microbescall_made
Rendueles O and GJ Velicer. 2017. The ISME Journal
external pageRapid and widespread de novo evolution of kin discriminationcall_made
Rendueles O, PC Zee, I Dinkelacker, M Amherd, S Wielgoss and GJ Velicer. 2015. PNAS
Social and multicellular phenotypes often evolve latently.
external pageHidden paths to endless forms most wonderful: ecology latently shapes evolution of multicellular development in predatory bacteriacall_made
M La Fortezza, O Rendueles, H Keller, GJ Velicer. 2022. Communications Biology
external pageAllopatric divergence of cooperators confers cheating resistance and limits effects of a defector mutationcall_made
KA Schaal, YTN Yu, M Vasse, GJ Velicer. 2022. BMC Ecology and Evolution
external pageHidden paths to endless forms most wonderful: Parasite-blind diversification of host qualitycall_made
L Freund, M Vasse, GJ Velicer. 2021. Proc Roy Soc B
external pageHidden paths to endless forms most wonderful: Complexity of bacterial motility shapes diversification of latent phenotypescall_made
O Rendueles, GJ Velicer. 2020. BMC Evolutionary Biology
external pageIndirect evolution of social fitness inequalities and facultative social exploitationcall_made
Nair RR, F Fiegna, GJ Velicer. 2018. Proc Roy Soc B
external pagePervasive, yet idiosyncrative, epistatic pleiotropy during adaptation in a behaviourally complex microbecall_made
Zee PC, J Liu and GJ Velicer. 2017. Journal of Evolutionary Biology
external pageRapid and widespread de novo evolution of kin discriminationcall_made
Rendueles O, PC Zee, I Dinkelacker, M Amherd, S Wielgoss and GJ Velicer. 2015. PNAS
external pageNon-adaptive processes can create the appearance of facultative cheating in microbescall_made
Smith J, JD van Dyken and GJ Velicer. 2013. Evolution
external pageDevelopmental cheating in the social bacterium Myxococcus xanthuscall_made
Velicer GJ, L Kroos and RE Lenski. 2000. Nature
We investigate the molecular mechanisms of some evolutionary outcomes that emerge in experimental populations.
external pageBacterial predator-prey coevolution selects on virulence-associated prey defensescall_made
Nair RR, Vasse M, Wielgoss S, Sun L, Yu YN, Velicer GJ. 2019. Nature Communications
external pageEvolution by flight and fight: diverse mechanisms of adaptation by actively motile microbescall_made
Rendueles O and GJ Velicer. 2017. The ISME Journal
external pageRapid and widespread de novo evolution of kin discriminationcall_made
Rendueles O, PC Zee, I Dinkelacker, M Amherd, S Wielgoss and GJ Velicer. 2015. PNAS
external pageA shift from magnitude to sign epistasis during adaptive evolution of a bacterial social traitcall_made
Zee PC, H Mendes-Soares, YTN Yu, H Keller, SA Kraemer, S Ossowski, K Schneeberger and GJ Velicer. 2014. Evolution
external pageAdaptive evolution of an sRNA that controls Myxococcus developmentcall_made
Yu YTN, X Yuan and GJ Velicer. 2010. Science
external pageNovel transcriptome patterns accompany evolutionary reversion of defective social development in the bacterium Myxococcus xanthuscall_made
Kadam SV, S Wegener-Feldbrügge, L Søgaard-Andersen and GJ Velicer. 2008. Molecular Biology and Evolution
external pageComprehensive mutation identification in an evolved bacterial cooperator and its cheating ancestorcall_made
Velicer GJ, G Raddatz, H Keller, S Deiss, C Lanz, I Dinkelacker and SC Schuster. 2006. PNAS
external pageEvolution of novel cooperative swarming in the bacterium Myxococcus xanthuscall_made
Velicer GJ and YTN Yu. 2003. Nature
external pageRescue of social motility lost during evolution of Myxococcus xanthus in an asocial environmentcall_made
Velicer GJ, RE Lenski and L Kroos. 2002. Journal of Bacteriology
We use experimental evolution to investigate how predation by and of myxobacteria shapes microbial communities.
external pageBacterial predation of a fungal wheat pathogen: Prelude to experimental evolution of enhanced biocontrol agentscall_made
SA Eisner, F Fiegna, BA McDonald, GJ Velicer. 2023. Plant Pathology
external pageHidden paths to endless forms most wonderful: ecology latently shapes evolution of multicellular development in predatory bacteriacall_made
M La Fortezza, O Rendueles, H Keller, GJ Velicer. 2022. Communications Biology
external pagePredatory bacteria select for sustained prey diversitycall_made
RR Nair, GJ Velicer. 2021. Microorganisms
external pageBacterial predator-prey coevolution selects on virulence-associated prey defensescall_made
Nair RR, M Vasse, S Wielgoss, L Sun, Y-TN Yu, GJ Velicer. 2019. Nature Communications
external pageExperimental evolution of a microbial predator’s ability to find preycall_made
Hillesland KL, GJ Velicer and RE Lenski. 2009. Proc Roy Soc B
external pageBacterial predatorscall_made
Velicer GJ and H Mendes Soares. 2009. Current Biology
external pageEvolution by flight and fight: diverse mechanisms of adaptation by actively motile microbescall_made
Rendueles O and GJ Velicer. 2017. The ISME Journal
external pageEvolution of an obligate social cheater to a superior cooperatorcall_made
Fiegna F, YTN Yu, SV Kadam and GJ Velicer. 2006. Nature
external pageEvolution of novel cooperative swarming in the bacterium Myxococcus xanthuscall_made
Velicer GJ and YTN Yu. 2003. Nature
external pageMutation rate and effective population size of the model cooperative bacterium Myxococcus xanthuscall_made
S Wielgoss, JD Van Dyken, GJ Velicer. 2024. Genome Biology and Evolution
external pageBacterial predator-prey coevolution accelerates genome evolution and selects on virulence-associated prey defencescall_made.
Nair RR, Vasse M, Wielgoss S, Sun L, Yu YN, Velicer GJ. 2019. Nature Communications
external pageGroup formation: on the evolution of aggregative multicellularitycall_made
M La Fortezza, KA Schaal, GJ Velicer. 2022. The evolution of multicellularity
external pageEvolution: Bacterial territoriality as a byproduct of kin discriminatory warfarecall_made
Velicer GJ and J Plucain. 2016. Current Biology
external pageHow do microbial populations and communities function as model systems?call_made
O’Malley MA, M Travisano, GJ Velicer and JA Bolker. 2015. The Quarterly Review of Biology
Whence comes social diversity? Ecological and evolutionary analysis of the myxobacteria
Velicer GJ, H Mendes-Soares and S Wielgoss. 2014. In Myxobacteria: Genomics and Molecular Biology, P. Higgs and Z. Yang eds. Horizon Scientific Press.
external pageSociobiology of the myxobacteriacall_made
Velicer GJ and M Vos. 2009. Annual Review of Microbiology
Why cooperate? The ecology and evolution of myxobacteria
Velicer GJ and KL Hillesland. 2007. In Myxobacteria: Multicellularity and Differentiation, D. Whitworth, editor. American Society for Microbiology Press.
external pageStrategies of microbial cheater controlcall_made
Travisano M and GJ Velicer. 2004. Trends in Microbiology
external pageSocial strife in the microbial worldcall_made
Velicer GJ 2003. Trends in Microbiology
external pageExperimental social evolution with Myxococcus xanthuscall_made
Velicer GJ and KL Stredwick. 2002. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
external pageGames microbes playcall_made
Lenski RE and GJ Velicer. 2000. Selection
